





- Introduction
- Function Introduction
- Performance Monitor
- Fusion Hunter
- Quantitative Chart
- SEC Filing
- Insider Trading (Search by Ticker)
- Insider Trading (Search by Reporter)
- Insider Trading (Top Insider Trading)
- Institutional Holdings
- Investment Trends (Investment Company List)
- Investment Trends (Sector & Industry Sentiment)
- Investment Trends (Investment Company Sentiment)
- Investment Trends (Top Institutional Trading)
- Investment Trends (Top Institutional Hldg Change)
- Key Ratio Distribution
- Screener
- Financial Statement
- Key Metrics
- High Current Difference
- Low Current Difference
- Relative Strength Index
- KDJ
- Bollinger Bands
- Price Earnings Ratio
- Price to Book Value
- Debt Equity Ratio
- Leverage Ratio
- Return on Equity
- Return on Assets
- Gross Margin
- Net Profit Margin
- Operating Margin
- Income Growth
- Sales Growth
- Quick Ratio
- Current Ratio
- Interest Coverage
- Institutional Ownership
- Sector & Industry Classification
- Data Portal
- API
- SEC Forms
- Form 4
- Form 3
- Form 5
- CT ORDER
- Form 13F
- Form SC 13D
- Form SC 14D9
- Form SC 13G
- Form SC 13E1
- Form SC 13E3
- Form SC TO
- Form S-3D
- Form S-1
- Form F-1
- Form 8-k
- Form 1-E
- Form 144
- Form 20-F
- Form ARS
- Form 6-K
- Form 10-K
- Form 10-Q
- Form 10-KT
- Form 10-QT
- Form 11-K
- Form DEF 14A
- Form 10-D
- Form 13H
- Form 24F-2
- Form 15
- Form 25
- Form 40-F
- Form 424
- Form 425
- Form 8-A
- Form 8-M
- Form ADV-E
- Form ANNLRPT
- Form APP WD
- Form AW
- Form CB
- Form CORRESP
- Form DSTRBRPT
- Form EFFECT
- Form F-10
- Form F-3
- Form F-4
- Form F-6
- Form F-7
- Form F-9
- Form F-n
- Form X-17A-5
- Form F-X
- Form FWP
- Form G-405
- Form G-FIN
- Form MSD
- Form N-14
- Form N-18F1
- Form N-18F1
- Form N-30B-2
- Form N-54A
- Form N-8A
- Form N-CSR
- Form N-MFP
- Form N-PX
- Form N-Q
- Form TTW
- Form TA-1
- Form T-3
- Form SC 14F1
- Form SE
- Form SP 15D2
- Form SUPPL
- Form 10-12G
- Form 18-K
- Form SD
- Form STOP ORDER
- Form TH
- Form 1
- Form 19B-4(e)
- Form 40-APP
- Form 497
- Form ABS-15G
- Form DRS
- Form MA
- Form UNDER
- AI sentiment
- Access guide
- Academy
- Term of service
- GDPR compliance
- Contact Us
- Question Center
| Font Size: |
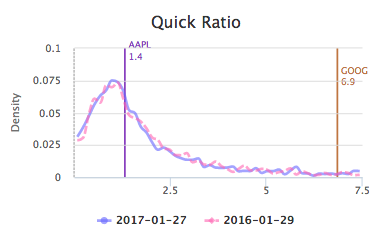
Quick Ratio
Quick ratio measures the ability of a company to meet its short term liabilities. It is calculated as (Current Assets - Inventories)/Current Liabilities (or alternatively, (Cash + Marketable Securities + Accounts Receivable) / Current Liabilities). Quick ratio is a more stringent measure of the liquidity of a company than current ratio, which does not remove inventories from the numerator. The higher the quick ratio, the better the liquidity of a company. In Katelynn's Report, higher quick ratio represents better performance (i.e. higher quantile ranking).
Generally quick ratio higher than 1 is a more preferred financial condition, irrespective of the sector or industry of a business. There is no significant differences in the distribution of quick ratio in different sectors and industries. At whole market level, 69%(as of 2017-01-27) companies have quick ratio higher than 1 (see figure below). Nevertheless, quick ratio less than 1 should not be a big concern for companies who can quickly turn inventories into cash or cash equivalent. Note that quick ratio makes several assumptions. 1) accounts receivable are readily available for collection. 2) no working capital is needed to maintain operations. These assumptions can not always be met for some companies.
 |